Starting with V10.0, Cora SeQuence has been renamed to Cora Orchestration.
V9.7.1 and later
Overview
For most File Activities, you need to define a connection to an external storage system. Depending on the activity, you will save a file, retrieve a file, delete a file, or create a folder in the external storage system.
NOTES
- Connection names and descriptions should be meaningful. You might want to use a connection in other activities, so it's important for you to be able to identify and understand what a connection is from the name and description.
- The path separator requirements for each storage system must also be used for base paths, source paths, file paths, and so on, in activities that require a connection to an external storage system. For example, if the file storage system you select supports forward slash (/) path separators, then all subsequent paths must also use forward slashes:https://{externalstoragesystem/{basepath}/{relativepath}/{file}
File activities that use an external storage system
- Put File Activity
- Get File Activity
- Get File Info Activity (V10.6 onwards)
- Create Folder Activity
- Delete File Activity
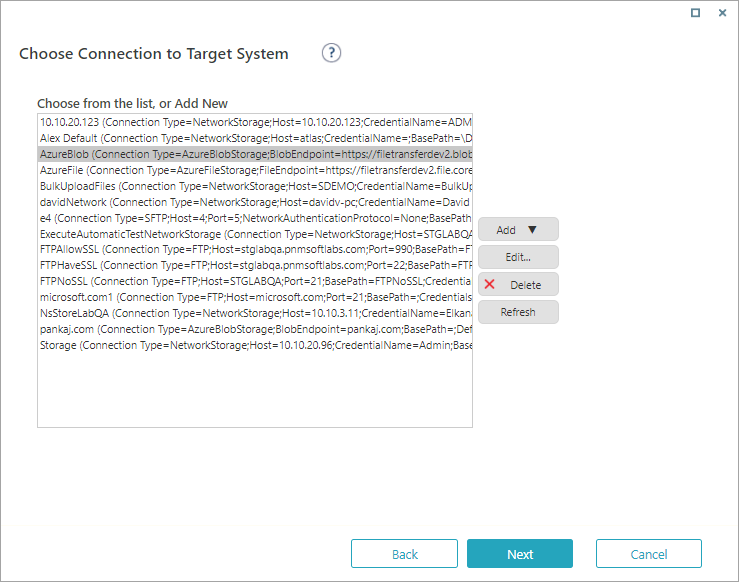
Supported external storage systems
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (AWS S3)
- Azure Blob Storage
- Azure File Storage
- FTP
- Network Storage
- SFTP
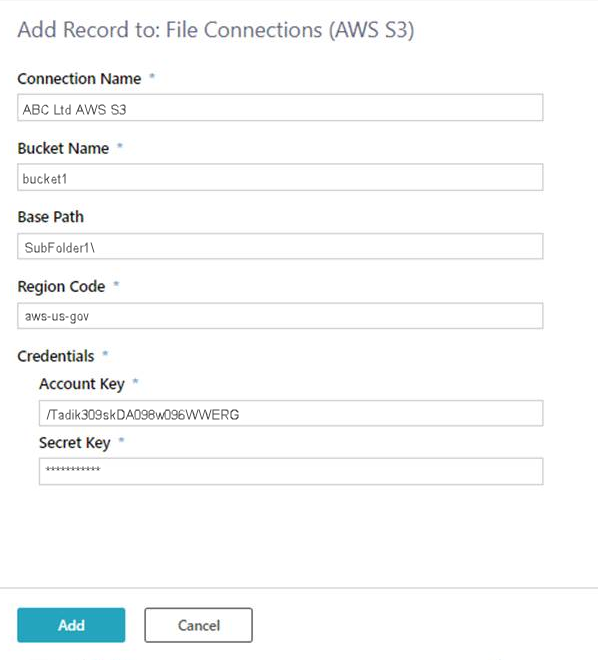
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
Specifications and limitations
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern | S3DirectoryInfo.GetFiles (string, SearchOption) |
| Path and File Name Restrictions | https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/bucketnamingrules.html |
| Path Separator | / |
| Supports Folder Hierarchy | No |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | The name you select for the connection. |
| Bucket Name | The S3 bucket name, where files are stored. |
| Base Path | The sub folder name. |
| Region Code | The region to which bucket is assigned. |
| Credentials |
|
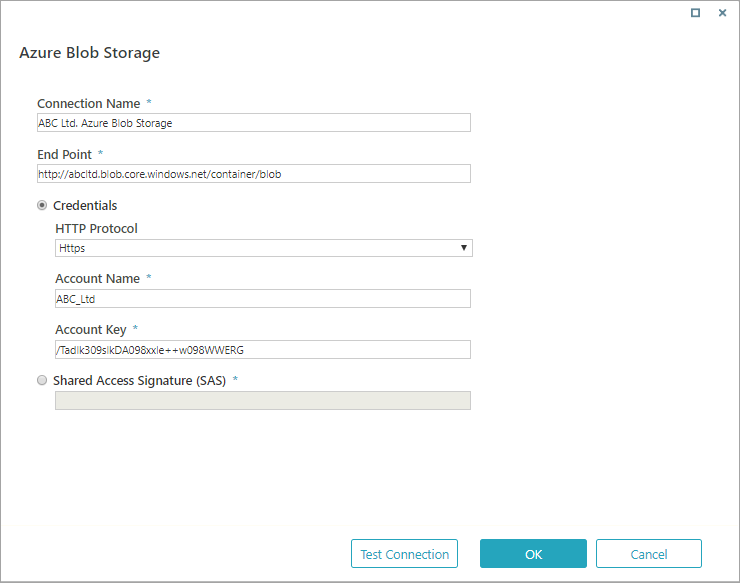
Azure Blob Storage
Specifications and limitations
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern | CloudBlobContainer.ListBlobs Method: a string containing the blob name prefix. |
| Path and File Name Restrictions | Naming and Referencing Shares, Directories, Files, and Metadata |
| Path Separator | / |
| Supports Folder Hierarchy | No, each container can only contain blobs. |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | The name you select for the connection. |
| End Point | URL to the Azure Blob storage. |
| Credentials | The protocol, account name, and account key for your Azure Blob Storage account. If you select this, SAS is not relevant. |
| Shared Access Signature (SAS) | Signature that grants limited access to objects in the storage account (system) to other clients, without exposing your account key. If you select this, Credentials is not relevant. |
NOTE
To make sure that you defined connection settings correctly, test the connection after you enter the required parameters.
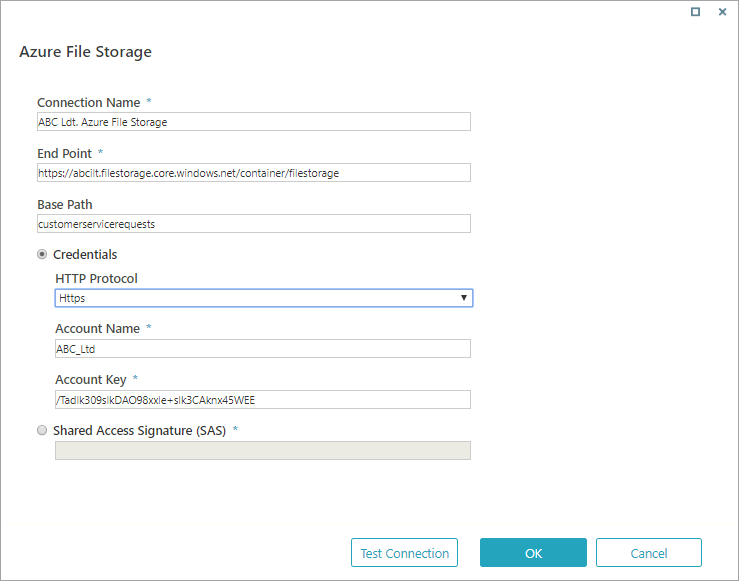
Azure File Storage
Specifications and limitations
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern | CloudFileDirectory.ListFilesAndDirectories Method: a string containing the file or directory name prefix. |
| Path and File Name Restrictions | Naming and Referencing Shares, Directories, Files, and Metadata. |
| Path Separator | / |
| Supports Folder Hierarchy | Yes |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | The name you select for the connection. |
| End Point | URL to the Azure Blob storage. |
| Base Path | Sub-folder in the end point. Should be a shared folder on the server. |
| Credentials | The protocol, account name, and account key for your Azure File Storage account. If you select this, SAS is not relevant. |
| Shared Access Signature (SAS) | Signature that grants limited access to objects in the storage account (system) to other clients, without exposing your account key. If you select this, Credentials is not relevant. |
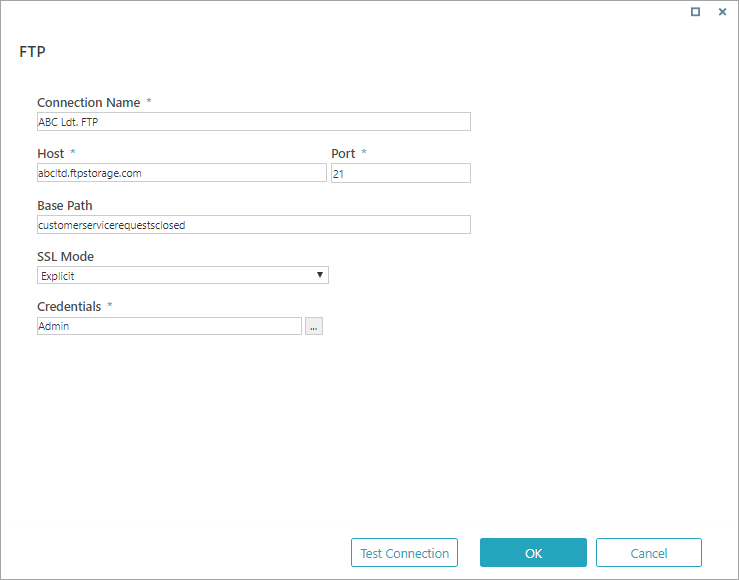
FTP
Specifications and limitations
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern |
|
| Path and File Name Restrictions | FTP does not specify a standard pathname convention. You need to follow the file-naming conventions of the file systems involved in the file transfer. |
| Path Separator | / |
| Supports Folder Hierarchy | Yes |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | The name you select for the connection. |
| Host | URL to the FTP server. |
| Port | Port for the FTP server. |
| Base Path | Sub-folder in the FTP server. Should be a shared folder on the server. Make sure the user defined in the credentials has permission on the shared folder. |
| SSL Mode |
|
| Credentials | Name, user name, and password for the FTP server. See screenshot below for details. |
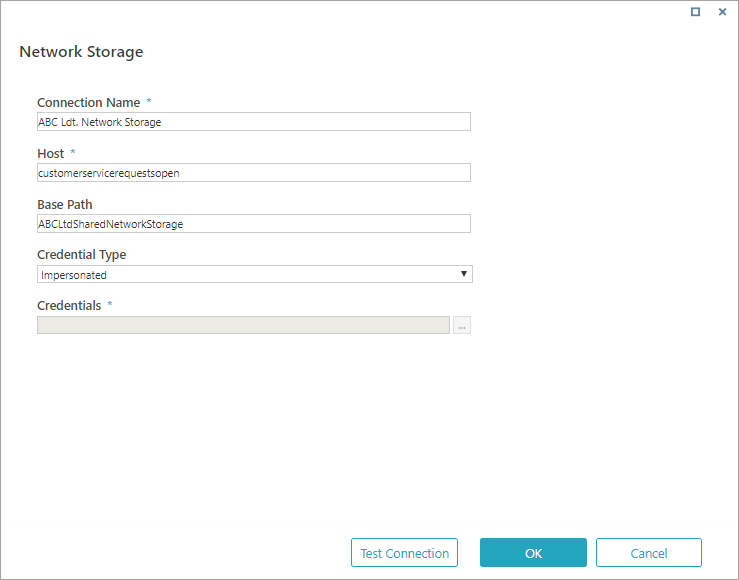
Network Storage
Specifications and limitations
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern | Directory.GetFiles Method |
| Path and File Name Restrictions | |
| Path Separator | \ |
| Supports Folder Hierarchy | Yes |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | The name you select for the connection. |
| Host | Name or URL of the network. |
| Base Path | Sub-folder in the network storage. Should be a shared folder on the server. Make sure the user defined in the credentials has permission on the shared folder. You cannot store files in the base path (folder). You need to a folder below this one to store files. |
| Credential Type |
|
| Credentials | Name, user name, and password for the FTP server. See screenshot below for details. |
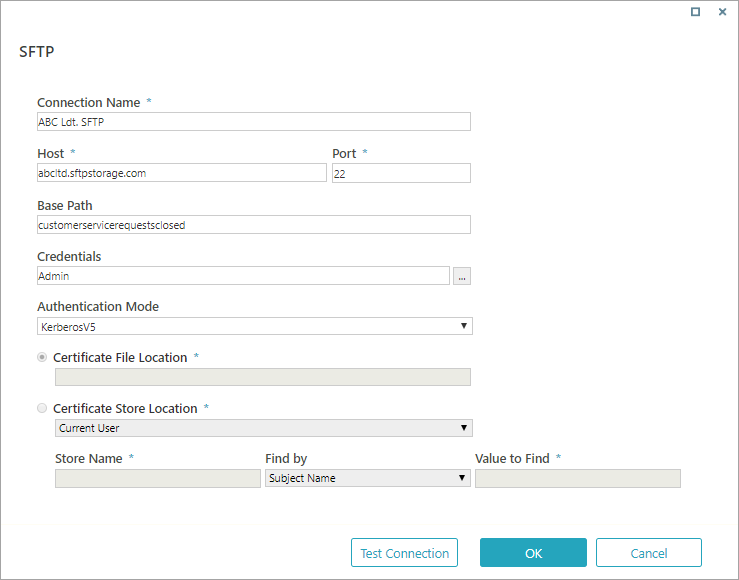
SFTP
Specifications and limitations
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern |
|
| Path and File Name Restrictions | FTP does not specify a standard pathname convention. You need to follow the file-naming conventions of the file systems involved in the file transfer. |
| Path Separator | / |
| Supports Folder Hierarchy | Yes |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | The name you select for the connection. |
| Host | URL to the SFTP server. |
| Port | Port for the SFTP server. |
| Base Path | Sub-folder in the SFTP server. Should be a shared folder on the server. Make sure the user defined in the credentials has permission on the shared folder. |
| SSL Mode |
|
| Credentials | Name, user name, and password for the FTP server. See screenshot below for details. |
| Authentication Mode |
|
| Certificate File Location | Path for the certificate. |
| Certificate Store Location | Path for the certificate store. |
| Store Name | Name of the certificate store. |
| Find by | Parameter to search by. |
| Value to Find | Value you want to find. |
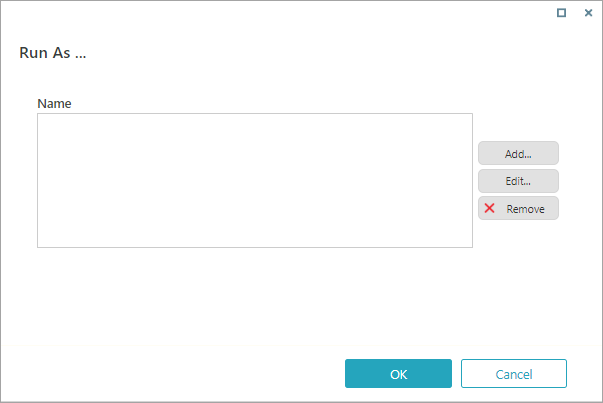
Credentials
Some external storage systems require credentials. The procedure to add a new credential is the same for every external storage system.
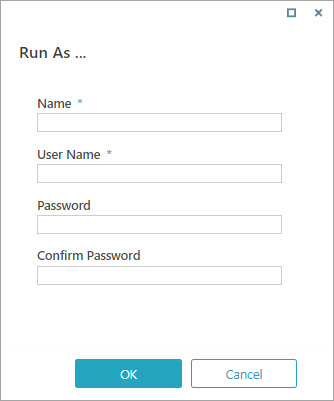
V8.7 and earlier
For most File Activities, you need to define a connection to an external storage system. Depending on the activity, you will save a file, retrieve a file, delete a file, or create a folder in the external storage system.
NOTES:
- Connection names and descriptions should be meaningful. You might want to use a connection in other activities, so it's important for you to be able to identify and understand what a connection is from the name and description.
- The path separator requirements for each storage system must also be used for base paths, source paths, file paths, and so on, in activities that require a connection to an external storage system. For example, if the file storage system you select supports forward slash (/) path separators, then all subsequent paths must also use forward slashes:https://{externalstoragesystem/{basepath}/{relativepath}/{file}
File activities that use an external storage system
Supported external storage systems
- Azure Blob Storage
- Azure File Storage
- FTP
- Network Storage
- SFTP

Azure Blob Storage
Specifications and limitations
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern | CloudBlobContainer.ListBlobs Method: a string containing the blob name prefix. |
| Path and File Name Restrictions | Naming and Referencing Shares, Directories, Files, and Metadata |
| Path Separator | / |
| Supports Folder Hierarchy | No, each container can only contain blobs. |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | The name you select for the connection. |
| End Point | URL to the Azure Blob storage. |
| Credentials | The protocol, account name, and account key for your Azure Blob Storage account. If you select this, SAS is not relevant. |
| Shared Access Signature (SAS) | Signature that grants limited access to objects in the storage account (system) to other clients, without exposing your account key. If you select this, Credentials is not relevant. |

Note:
To make sure that you defined connection settings correctly, test the connection after you enter the required parameters.
Azure File Storage
Specifications and limitations
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern | CloudFileDirectory.ListFilesAndDirectories Method: a string containing the file or directory name prefix. |
| Path and File Name Restrictions | Naming and Referencing Shares, Directories, Files, and Metadata |
| Path Separator | / |
| Supports Folder Hierarchy | Yes |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | The name you select for the connection. |
| End Point | URL to the Azure Blob storage. |
| Base Path | Sub-folder in the end point. Should be a shared folder on the server. |
| Credentials | The protocol, account name, and account key for your Azure File Storage account. If you select this, SAS is not relevant. |
| Shared Access Signature (SAS) | Signature that grants limited access to objects in the storage account (system) to other clients, without exposing your account key. If you select this, Credentials is not relevant. |

FTP
Specifications and limitations
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern |
|
| Path and File Name Restrictions | FTP does not specify a standard pathname convention. You need to follow the file-naming conventions of the file systems involved in the file transfer. |
| Path Separator | / |
| Supports Folder Hierarchy | Yes |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | The name you select for the connection. |
| Host | URL to the FTP server. |
| Port | Port for the FTP server. |
| Base Path | Sub-folder in the FTP server. Should be a shared folder on the server. Make sure the user defined in the credentials has permission on the shared folder. |
| SSL Mode |
|
| Credentials | Name, user name, and password for the FTP server. See screenshot below for details. |
Network Storage
Specifications and limitations
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern | Directory.GetFiles Method |
| Path and File Name Restrictions | |
| Path Separator | \ |
| Supports Folder Hierarchy | Yes |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | The name you select for the connection. |
| Host | Name or URL of the network. |
| Base Path | Sub-folder in the network storage. Should be a shared folder on the server. Make sure the user defined in the credentials has permission on the shared folder. You cannot store files in the base path (folder). You need to a folder below this one to store files. |
| Credential Type |
|
| Credentials | Name, user name, and password for the FTP server. See screenshot below for details. |

SFTP
Specifications and limitations
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern |
|
| Path and File Name Restrictions | FTP does not specify a standard pathname convention. You need to follow the file-naming conventions of the file systems involved in the file transfer. |
| Path Separator | / |
| Supports Folder Hierarchy | Yes |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | The name you select for the connection. |
| Host | URL to the SFTP server. |
| Port | Port for the SFTP server. |
| Base Path | Sub-folder in the SFTP server. Should be a shared folder on the server. Make sure the user defined in the credentials has permission on the shared folder. |
| SSL Mode |
|
| Credentials | Name, user name, and password for the FTP server. See screenshot below for details. |
| Authentication Mode |
|
| Certificate File Location | Path for the certificate. |
| Certificate Store Location | Path for the certificate store. |
| Store Name | Name of the certificate store. |
| Find by | Parameter to search by. |
| Value to Find | Value you want to find. |

Credentials
Some external storage systems require credentials. The procedure to add a new credential is the same for every external storage system.